Because hearing loss can develop over several years, most people are not aware of the extent of their hearing loss until family or friends bring it to their attention. Even then, the problem is often ignored or explained with excuses such as fatigue or “people are mumbling”.
Recognizing a hearing loss in yourself or someone you know is the first step toward improving the situation.
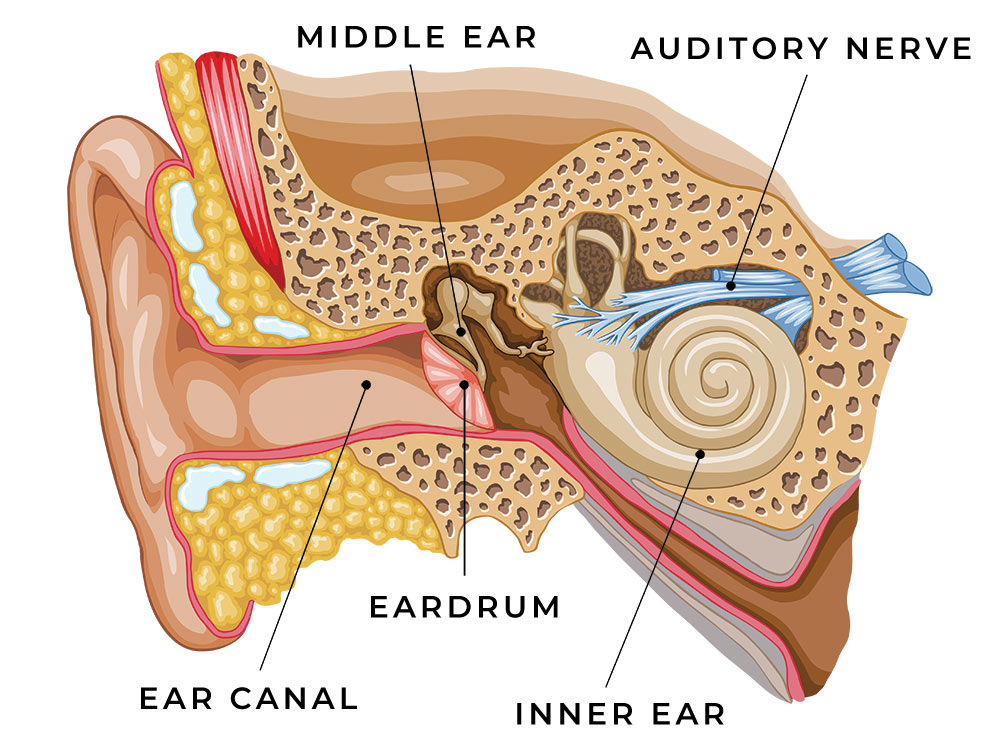
There are three types of hearing loss: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed.
A conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the ear canal, eardrum or middle ear.
This type of hearing loss has the potential to be corrected surgically or can also be helped with hearing aids.
A sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve. Damage can be caused by:
Hearing loss of this type is typically a permanent and can usually be helped with hearing aids.
A mixed hearing loss occurs when someone has a combination of a sensorineural hearing loss and a conductive hearing loss.
Numerous studies have linked untreated hearing loss to a wide range of physical and emotional conditions. These include impaired memory and ability to learn new tasks, reduced alertness, increased risk to personal safety, irritability, negativism, anger, fatigue, tension, stress, depression, and diminished psychological and overall health, as well as economic disadvantages. Fortunately, the vast majority of people with hearing loss can be helped with hearing aids. Recent studies showed that nine out of ten hearing aid users report improvements in their quality of life.
Do you hear a ringing, roaring, clicking, or hissing sound in your ears? Do you hear this sound often or all the time? Does the sound bother you a lot? If you answer yes to these questions, you may have tinnitus.
Tinnitus is a symptom associated with many forms of hearing loss. It can also be a symptom of other health problems.
The first step is to see an Audiologist for an evaluation. A careful history and audiometric testing will lead to the most likely causes and best treatment for your tinnitus. You may be referred to an ear, nose and throat examination to complete the diagnosis.
Although there is no cure for tinnitus, researchers have discovered several treatments that may give you some relief. Not every treatment works for everyone, so you may need to try several to find the ones that help.
Many people find listening to music very helpful. Focusing on music might help you forget about your tinnitus for a while. It can also help to mask the sound. Other people like to listen to recorded nature sounds, like ocean waves, the wind, or even crickets.
Avoid anything that can make your tinnitus worse, such as smoking, alcohol and loud noise. If you are a construction worker, an airport worker, or a hunter, or if you are regularly exposed to loud noise at home or at work, wear ear plugs or special earmuffs to protect your hearing and keep your tinnitus from getting worse.
Schedule an appointment with an Audiologist to evaluate and discuss your tinnitus.
Hearing aids.
Most people with tinnitus have some degree of hearing loss. Hearing aids create a dual benefit of enhancing hearing and masking or covering up the tinnitus. The majority of patients with tinnitus receive partial or complete relief from their tinnitus with the use of hearing aids.
Maskers.
Tinnitus maskers are small electronic devices that look like hearing aids and are tuned to generate sound that masks or covers up the tinnitus. Like hearing aids, they may provide relief from the tinnitus, but will not enhance hearing and may interfere with understanding speech.
Many types of devices, such as fans, radios and sound generators can be used as tinnitus maskers to help tinnitus sufferers to fall sleep or get back to sleep.
Medicine or drug therapy.
Some tinnitus sufferers develop anxiety and other strong emotional responses to their tinnitus. Certain medicines may provide relief from these emotional reactions and provide some relief from the tinnitus. Other medicines and nutritional supplements have provided relief in some patients.
Counseling.
People with tinnitus may experience anxiety, depression and other psychiatric problems. You may be referred to a psychiatrist our counselor as needed.
Relaxing.
Learning how to relax is very helpful if the noise in your ears frustrates you. Stress makes tinnitus seem worse. By relaxing, you have a chance to rest and better deal with the sound.